Neurology - Jones 2E
Author: H. Royden Jones
ISBN: 9781437702736
Initial Clinical Evaluation
- Page 5: Cranial Nerves: Distribution of Motor and Sensory Fibers
- Page 6: Cranial Nerves: Nerves and Nuclei
- Page 7: Visual Pathways: Retina to Occipital Cortex
- Page 8: Anatomic Innervation of the Eye
- Page 9: Right Horner Syndrome
- Page 10: Effects of Increased Intracranial Pressure On Optic Disk and Visual Fields
- Page 11: Control of Eye Movements
- Page 12: Trigeminal Nerve Neuralgia
- Page 13: Facial Nerve with its Muscle Innervation
- Page 14: Vestibular Eighth Nerve Input to Horizontal Eye Movements and Nystagmus
- Page 15: Auditory Nerve Testing: Weber and Rinne Testing
- Page 15: Test for Positional Vertigo
- Page 16: Uvula, Tongue, and Vocal Cord Weakness
- Page 17: Gait Disorder Characteristics and Etiology
- Page 18: Pyramidal System, Corticospinal Tract
- Page 20: Primary Sites of Motor Disorders
- Page 22: Dermatomal Levels
- Page 24: Cutaneous Innervations
- Page 25: Motor Tone Abnormality
- Page 26: Cerebellar Afferent Pathways
- Page 27: Muscle and Joint Receptors and Muscle Spindles
- Page 27: Elicitation of the Babinski Sign
- Page 28: Documentation of Various Types of Sensory Modalities In a Peripheral Neuropathy
- Page 29: Somesthetic System: Body
- Page 30: Thalamus and Its Multiple Nuclei
- Page 32: Cerebral Cortex (Superolateral Surface)
- Page 33: Cerebral Cortex: Localization of Function and Association Pathways
- Page 35: Brodmann Areas: Lateral View of the Forebrain
- Page 36: Major Limbic Forebrain Cingulate Cortex Areas
- Page 37: Cerebral Insular Cortex
- Page 38: Cerebral Cortex (Medial Surface)
- Page 40: Testing for Defects of Higher Cortical Function
- Page 43: Nondominant Hemisphere Higher Cortical Function
- Page 44: Cerebral Cortex (Medial Surface of Brain Lobes and Functional Areas)
- Page 45: Cerebral Cortex (Inferior Surface)
- Page 46: Occipital Lobe Functional Anatomy
- Page 47: Dominant Hemisphere Language Dysfunction
- Page 48: Structural Anatomy of Word-Finding Difficulty In Degenerative Disorders
Cranial Nerves
- Page 53: Olfactory Receptors
- Page 54: Olfactory Pathways
- Page 55: Subfrontal Meningioma
- Page 58: The Retina and the Photoreceptors
- Page 59: Retinal Architecture and Perimetry
- Page 60: Anatomy of the Optic Nerve (Clinical Appearance)
- Page 61: Giant Cell Arteritis: Ocular Manifestations
- Page 61: Optic Disc and Visual Field Changes In Glaucoma
- Page 62: Multiple Sclerosis: Ocular Manifestations
- Page 65: Anatomy and Relations of Optic Chiasm
- Page 66: Pituitary Macroadenoma
- Page 67: Disorders Affecting Optic Chiasm
- Page 68: Posterior Visual Pathway and Connections
- Page 68: Topographic Representation of the Visual Fields Across the Optic Pathway
- Page 69: Arteries of Brain: Inferior Views
- Page 70: Occipital Cortex and Projections
- Page 71: Arteries of Brain (Lateral and Medial Views)
- Page 72: Left Posterior Cerebral Infarction
- Page 76: Oculomotor (III), Trochlear (IV) and Abducent (VI) Nerves: Schema
- Page 77: Ophthalmologic Manifestations of Cerebral Aneurysms
- Page 78: Aneurysms Causing Oculomotor Nerve Palsy
- Page 81: Extraocular Muscles and General Function
- Page 83: Central Control of Eye Movements
- Page 88: Parasympathetic Pupillary Innervation and the Light Reflex Pathway
- Page 89: Sympathetic Pupillary Innervation
- Page 93: Trigeminal Nerve (V): Schema
- Page 94: Ophthalmic (V1), Maxillary (V2), and Mandibular (V3) Nerves
- Page 95: Cranial Nerve Nuclei In Brainstem: Schema
- Page 96: Trigeminal Sensory Components
- Page 96: Mandibular Nerve (V3) Sensory and Motor
- Page 97: Acoustic Neurinoma Compressing Trigeminal Nerve
- Page 97: Varicella Zoster With Probable Keratitis
- Page 99: Facial Nerve Schema and Intracranial Course
- Page 100: Central Versus Peripheral Facial Paralysis
- Page 101: Bell's Palsy
- Page 102: Cerebellopontine Angle Tumor
- Page 103: Facial Nerve Branches and Parotid Gland
- Page 106: Seventh Nerve Hemangioma
- Page 107: Imaging of Bell Palsy
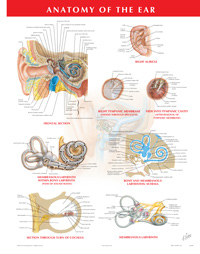
- Page 110: Pathway of Sound Reception
- Page 111: Afferent Auditory Pathways
- Page 112: Hearing Tests: Weber and Rinne
- Page 112: Vestibular Schwannoma
- Page 115: Causes of Vertigo (Classified by Region)
- Page 115: Vestibular Receptors
- Page 117: Canalith Repositioning (Epley) Maneuver
- Page 122: Neuroregulation of Deglutition
- Page 124: Glossopharyngeal Nerve (IX): Schema
- Page 125: Vagus Nerve (X): Schema
- Page 126: Deglutition
- Page 127: Innervation of Larynx
- Page 128: Glomus Tumor of Vagal Nerve
- Page 131: Accessory Nerve (XI): Schema
- Page 131: Cervical Plexus In Situ
- Page 132: Clinical Findings In Cranial Nerve XI Damage
- Page 134: Hypoglossal Nerve (XII): Schema
- Page 134: Hypoglossal Nerve Intermedullary Course
- Page 135: Base of Skull
- Page 136: Hypoglossal Nerve (XII)
- Page 137: Glomus Jugulare With Hypoglossal Palsy
Headache and Pain
- Page 141: Pain: Sensitive Structures and Pain Referral
- Page 142: Mechanisms in Migraine
- Page 143: Migraine
- Page 143: Pathophysiology of Migraine and Triptan Site of Action
- Page 145: Cluster Headache and Chronic Paroxysmal Hemicrania
- Page 146: Muscle Contraction Headache
- Page 149: Giant-Cell (Temporal) Arteritis, Polymyalgia Rheumatica
- Page 150: Pseudotumor Cerebri
- Page 151: Low-Pressure Headache
- Page 153: Suboccipital Triangle
- Page 156: Mechanisms of Neuropathic Pain and Sympathetically Maintained Pain
- Page 157: Pain Pathway
- Page 158: Serotonin Synapses of Pain Pathways
- Page 158: Opioids: Receptor - Transduction Mechanisms
- Page 160: Diabetes Mellitus and Neuropathy
- Page 161: Foot Complications in Diabetic Neuropathy
- Page 162: Reflex Sympathetic Dystrophy
Attention and Consciousness
- Page 167: Cholinergic (C) and Adrenergic (A) Synapses: Schema
- Page 168: Eye: Autonomic Innervation
- Page 168: Facial Nerve with its Muscle Innervation
- Page 169: Glossopharyngeal Nerve (IX): Schema
- Page 170: Vagus Nerve: Autonomic Innervation
- Page 171: Pelvic Organs: Autonomic Innervation
- Page 171: Symptoms of Dysautonomia
- Page 173: Syncope: Four-Step Management Approach
- Page 176: Origin and Spread of Seizures
- Page 177: Neuroimaging Studies
- Page 178: Simple Partial Seizures
- Page 179: Electroencephalography
- Page 180: Causes of Seizures
- Page 181: Generalized Tonic-Clonic Seizures
- Page 181: Absence (Petit Mal) Seizures
- Page 183: Status Epilepticus
- Page 188: Preoperative Evaluation
- Page 189: Resective Surgery
- Page 192: Sleep-Wakefulness Control
- Page 193: Sleep Disorders with Hypersomnia
- Page 195: REM Sleep Behavior Disorder
- Page 197: Glasgow Coma Scale
- Page 198: Differential Diagnosis of Coma
- Page 199: Initial Management of Coma and Severe Head Injuries
- Page 201: Prognosis In Coma Related to Severe Head Injuries
- Page 202: Persistent Vegetative State
- Page 204: Eye Movements in Coma
- Page 205: Respiratory Exchange in Head Injury
- Page 206: MR and CT Images Showing Cerebral Herniation Patterns
- Page 210: Hypoxic Brain Damage and Brain Death
Cognitive and Behavioral Disorders
- Page 222: Alzheimer Disease: Pathology
- Page 223: Distribution of Pathology In Alzheimer Disease
- Page 224: Amyloidogenesis in Alzheimer's Disease
- Page 225: Amyloid Cascade Hypothesis In Alzheimer's Disease
- Page 226: Microscopic Pathology In Alzheimer's Disease
- Page 227: Risk Factors for Alzheimer's Disease
- Page 228: Possible Factors in Development and Progression of Alzheimer's Disease
- Page 229: Alzheimer Disease: Clinical Manifestations, Progressive Phases
- Page 230: Treatable Dementias
- Page 231: Nondominant Hemisphere Cortical Dysfunction
- Page 232: FDG-PET Typical Pattern for Alzheimer Disease
- Page 233: Daily Living Assessment
- Page 234: Pharmacologic Management
- Page 236: Dementia With Lewy Bodies
- Page 239: Lobar Dementias
- Page 242: Vascular Cognitive Impairment (VCI)-Type Dementia
- Page 246: Transmissible Spongiform Encephalopathy
Psychiatric Disorders
- Page 249: Alcohol Abuse
- Page 250: Signs Suggestive of Alcohol Abuse
- Page 251: Alcohol Dependence
- Page 252: Alcohol Withdrawal
- Page 252: Opioid Withdrawal
- Page 253: Benzodiazepine Withdrawal
- Page 259: Borderline Personality Disorder
- Page 261: Panic Disorder
- Page 266: Eating Disorders
- Page 267: Dysthymia
- Page 270: Major Depression in Seniors
- Page 271: The Face of Depression
- Page 272: Major Depression
- Page 275: Personality Disorders
- Page 276: Bipolar Affective Disorder: Manic Episode
Gait and Movement Disorders
- Page 288: Neuropathy of Parkinson's Disease
- Page 289: Parkinson Disease: Anatomy with Biochemical Pathways
- Page 290: Horizontal Brain Sections of Basal Ganglia
- Page 291: Parkonsionism: Hypothesized Role of Dopa
- Page 292: Clinical Signs of Parkinson Disease
- Page 296: Catecholamine Synthesis
- Page 309: Tremor
- Page 316: Chorea
- Page 317: Choreiform Movements
- Page 321: Wilson Disease
- Page 329: Common Motor Tics
- Page 332: Cervical Dystonia
- Page 337: Medication-Induced Parkinsonism
- Page 337: Acute Dystonic Reaction
- Page 338: Tardive Dyskinesia
Spinal Cord Disorders
- Page 347: Spinal Cord and Ventral Rami In Situ
- Page 348: Relation of Spinal Nerve Roots to Vertebrae
- Page 349: Principal Fiber Tracts of Spinal Cord
- Page 350: Spinal Cerebral Afferent Systems
- Page 351: Cerebral Cortex: Efferent Pathways
- Page 352: Arteries of Spinal Cord: Schema
- Page 352: Spinal Cord Cross Sections: Fiber Tracts
- Page 353: Arteries of Spinal Cord: Intrinsic Distribution
- Page 353: Veins of Spinal Cord and Vertebrae
- Page 354: Motor Impairment Related to Level of Spinal Cord Injury
- Page 355: Sensory Impairment Related to Elvel of Spinal Cord Injury
- Page 356: Incomplete Spinal Cord Syndromes
- Page 356: Acute Spinal Cord Syndromes Pathology
- Page 357: Syringomyelia
- Page 357: Intradural Extramedullary Tumors of Spinal Cord
- Page 357: Extradural Tumors
- Page 359: Acute Spinal Cord Syndromes: Evolution of Symptoms
- Page 360: Trauma
- Page 361: Cervical Disc Herniation
- Page 362: Idiopathic Spinal Stenosis
- Page 362: Metastatic Malignancies
- Page 363: Epidural Abscess and Epidural Hematoma
- Page 364: Myelitis Secondary to Neuromyelitis Optica (Devic) and Multiple Sclerosis
- Page 366: Spinal Cord Infarction
- Page 368: Cervical Spondylosis
- Page 368: Imaging of Ossification of Posterior Longitudinal Ligament (OPLL)
- Page 371: Spinal Arteriovenous Malformations
- Page 374: Subacute Combined Degeneration
- Page 375: Nutritional Myelopathies
- Page 380: Syringomyelia
- Page 382: Friedreich Ataxia
Multiple Sclerosis and Other Demyelinating Disorders
- Page 387: Multiple Sclerosis: Central Nervous System Pathology
- Page 390: Multiple Sclerosis: Ocular Manifestations of Multiple Sclerosis
- Page 391: Multiple Sclerosis: Cerebellar and Brain Stem Manifestations
- Page 392: Multiple Sclerosis: Myelopathic Manifestations
- Page 393: Brain MRI In Multiple Sclerosis
- Page 395: Spinal Cord MRI In Multiple Sclerosis
- Page 396: Multiple Sclerosis: Diagnostic Tests - Spinal Fluid
- Page 397: Tests for Multiple Sclerosis: Evoked Responses
- Page 403: Optic Nerve Atrophy
- Page 404: Neuromyelitis Optica
- Page 405: Acute Disseminated Encephalomyelitis
Infectious Disease
- Page 409: Bacterial Meningitis
- Page 410: Bacterial Meningitis
- Page 411: Parameningeal Infections
- Page 411: Multiple Brain Abscesses In a 32-Year-Old With Septicemia
- Page 414: Spinal Epidural Abscess
- Page 415: Lyme Disease Clinical Settings
- Page 417: Lyme Disease
- Page 418: Tuberculosis
- Page 420: Leprosy
- Page 422: Tetanus
- Page 424: Neurosyphilis
- Page 427: HSV Encephalitis
- Page 428: Herpes Simplex Encephalitis
- Page 430: Eastern Equine Encephalitis
- Page 431: Primary HIV Infection of the Nervous System
- Page 433: Herpes Zoster
- Page 435: Rabies
- Page 437: Poliomyelitis
- Page 438: Poliomyelitis
- Page 440: Geographic Distribution of Malaria
- Page 441: Treatment of Malaria
- Page 442: Trypanosomiasis: African Sleeping Sickness
- Page 444: Cysticerosis
- Page 445: Trichinosis
- Page 447: Neurosarcoidosis: MRI and Pathology
- Page 448: Sarcoidosis, Brucellosis, Histoplasmosis
- Page 451: Slow Virus Infections
- Page 452: Cryptococcosis and Listeriosis
- Page 453: Nocardiosis
- Page 454: Toxoplasmosis
Neuro-Oncology
- Page 459: Gliomas
- Page 461: Glioma MRI and Pathology
- Page 462: Gliomatosis Cerebri
- Page 462: Oligodendroglioma
- Page 464: Glioma, Anaplastic Astrocytoma
- Page 465: Primary CNS Lymphoma
- Page 466: Ependymoma
- Page 467: Medulloblastoma
- Page 468: Cystic Astrocytoma of Cerebellum
- Page 469: Brain Glioma
- Page 470: Tumors Metastatic to Brain
- Page 471: Pituitary Adenoma Clinical Manifestations
- Page 471: Meningiomas
- Page 472: Basophilic Adenoma Cushing Disease
- Page 473: Pituitary Macroadenoma
- Page 474: Pituitary Adenoma Gradation Vis-a-vis Sella Enlargement
- Page 475: Craniopharyngioma
- Page 476: Acoustic Neurinomas
- Page 477: Chordomas
- Page 478: Tumors of Pineal Region
- Page 479: Intraventricular Tumors
- Page 480: Pseudotumor Cerebri
- Page 481: Intracranial Hypotension
- Page 484: Myelographic and CT Characteristics of Spinal Tumors
- Page 485: Clinical Profile: Acute Spinal Cord Decompensation with an Epidural Tumor
- Page 485: Extradural Metastatic Spinal Tumors
- Page 486: Extradural Primary Malignant Spinal Tumors
- Page 487: Extradural Primary Benign Spinal Tumors
- Page 488: Intradural Extramedullary Primary Spinal Tumors
- Page 490: Intradural Intramedullary Primary Spinal Cord Tumors
Cerebrovascular Diseases
- Page 493: Arteries to Brain and Meninges
- Page 494: Arteries of Brain: Lateral and Medial Views
- Page 495: Arteries of Brain: Inferior Views
- Page 498: Atherosclerosis, Thrombosis, and Embolism
- Page 499: Role of Platelets in Arterial Thrombosis
- Page 500: Common Sites of Cerebrovascular Occlusive Disease
- Page 501: Cardiac Embolism
- Page 502: Lacunar Infarction
- Page 502: Arterial Dissection
- Page 503: Ocular Signs of Large Vessel Disease
- Page 504: Occlusion of Middle and Anterior Cerebral Arteries
- Page 506: Clinical Manifestations of Vertebrobasilar Territory Ischemia
- Page 507: Basilar Artery Occlusion
- Page 507: Occlusion of Top of Basilar and Posterior Cerebral Arteries
- Page 510: Intracranial Arterial Imaging With CT and MRI
- Page 511: Acute Ischemic Infarct With a Right Middle Cerebral Artery Clot
- Page 516: Endarterectomy for Extracranial of Carotid Artery Atherosclerosis
- Page 516: Cerebrovascular Emboli Protection Device
- Page 519: Dura Mater Venous Sinuses
- Page 520: Deep and Subependymal Veins of Brain
- Page 521: Subependymal Veins
- Page 522: Veins of Posterior Cranial Fossa
- Page 522: Cavernous Sinus and Its Cranial Nerves
- Page 523: Sagittal Sinus Thrombosis
- Page 524: Intracranial Complications
- Page 527: Right Middle Cerebral Artery Aneurysm
- Page 527: Middle Cerebral Artery Aneurysm Clipping
- Page 528: Basilar Artery Tip Aneurysmal Bleed
- Page 528: Basilar Artery Tip Aneurysm
- Page 529: Clinical Manifestations of Cerebral Aneurysm Rupture
- Page 530: Ophthalmologic Manifestations of Cerebral Aneurysms
- Page 531: Subarachnoid Hemorrhage
- Page 532: Typical Sites of Cerebral Aneurysms
- Page 532: Giant Cerebral Aneurysms
- Page 535: Frontotemporal Approach for Internal Cartoid, Ophthalmic, Anterior Communicating, and Anterior and Middle Cerebral Aneurysms
- Page 535: Posterior Approach for Vertebral and Posterior Inferior Cerebellar Aneurysms
- Page 536: Basilar Tip Aneurysm Re-expansion
Trauma
- Page 551: Glasgow Coma Scale
- Page 551: Basilar Skull Fractures
- Page 552: Signs Suggesting Need for Operation In Head Injuries
- Page 553: Epidural Hematoma
- Page 553: Compound Depressed Skull Fractures
- Page 554: Meningeal Arteries and Dura Mater
- Page 555: CT and Angiogram of ICH
- Page 556: Superficial Cerebral Veins and Diploic Veins
- Page 557: Acute Subdural Hematomas
- Page 558: Intensive Medical Management of Severe Head Injury
- Page 559: Persistent Vegetative State
- Page 559: Shear Injury
- Page 560: Exploratory Burr Holes and Removal of Posterior Fossa Hematoma
- Page 561: Brain Injury In Military Combat
- Page 563: Cervical Spine Injury: Compression
- Page 564: Cervical Spine Injury: Hyperextension
- Page 565: Cervical Spine Injury: Hyperextension Flexion-Rotation
- Page 566: Fracture and Dislocation of Cervical Vertebrae
- Page 567: Suspected Cervical Spine Injury: Treatment at Site of Accident
- Page 568: Dens Fracture of Cervical Spine
- Page 568: Cervical Spine Injury: Traction and Bracing
- Page 569: Plain Radiograph of Hangman's Fracture: Cervical Spine
- Page 569: Non-Axial Burst Fracture: Cervical Spine
- Page 570: Burst Fracture: Lumbar Spine
- Page 570: Cervical Spine Injury: Rehabilitation of Patient
Radiculopathies and Plexopathies
- Page 575: Dermatomes and Myotomes of Upper Limb
- Page 576: Cervical Disk Herniation: Clinical Manifestations
- Page 577: Extraspinal Tumor
- Page 577: Desmoid Tumor
- Page 578: Large Right Lateral C6-C7 Disc Herniation
- Page 578: Cervical Spinal Stenosis
- Page 580: L4-5 Role of Inflammation In Lumbar Pain
- Page 581: Lumbar Disc Herniation: Clinical Manifestations
- Page 582: Examination of Patient with Low Back Pain
- Page 583: Disc Extrusion
- Page 583: Pain Patterns in Lumbar Disease
- Page 584: Lumbar Spinal Stenosis
- Page 585: Intradural Spinal Tumors
- Page 585: Laminectomy and Discectomy
- Page 592: Brachial Plexopathy
- Page 593: Parsonage-Turner Brachial Plexitis
- Page 594: Anatomy of Brachial Plexus
- Page 595: Anatomy of Lumbar, Sacral, and Coccygeal Plexuses
- Page 597: Apical Lung Tumor Invading Left Brachial Plexus
- Page 597: Radiculoplexopathies
- Page 598: Large Hematoma
Mononeuropathies
- Page 601: Scapular, Axillary and Radial Nerves
- Page 602: Neuropathy About Shoulder
- Page 603: Cutaneous Innervation of the Upper Limb
- Page 604: Median Nerve
- Page 606: Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
- Page 607: Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
- Page 608: Proximal Compression of Median Nerve
- Page 609: Ulnar Nerve
- Page 610: Ulnar Tunnel Syndrome
- Page 611: Cubital Tunnel Syndrome
- Page 611: Compression of Ulnar Nerve
- Page 612: Radial Nerve in Forearm
- Page 613: Radial Nerve Compression
- Page 615: Electrodiagnostic Studies In Compression Neuropathy
- Page 618: Sciatic, Peroneal, and Tibial Nerves
- Page 619: Peroneal Nerve
- Page 620: Peroneal Nerve Schwannoma
- Page 621: Posterior Tibial Neurofibroma
- Page 623: Femoral Nerve and Lateral Femoral Cutaneous Nerves
- Page 623: Femoral Nerve Neurofibromas In Neurofibromatosis (Arrows)
- Page 624: Lateral Femoral Cutaneous Nerve
- Page 625: Obturator Nerve
Motor Neuron Disorders
- Page 631: Cerebral Cortex: Efferent Pathways
- Page 631: Corticobulbar Tract
- Page 633: Frontal Temporal Atrophy
- Page 633: Dorsal and Ventral Roots and Ventral Horn
- Page 634: Motor Neuron Disease: Early Clinical Manifestation
- Page 634: Tongue Atrophy In Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis
- Page 635: Head Drop in Amyotrophic Sclerosis
- Page 640: Motor Neuron Disease: Habilitation Devices
- Page 642: Spinal Muscular Atrophy Type 1
- Page 643: Pathologic Anatomy of Scoliosis
- Page 644: Hirayama Disease
- Page 646: Pathogenesis of Poliomyelitis
- Page 647: Poliomyelitis
- Page 649: Multifocal Motor Neuropathy
Neuromuscular Hyperactivity Disorders
- Page 653: Tetanus
- Page 653: Renshaw Cell Bias
- Page 653: Stiff Person Syndrome
Polyneuropathies
- Page 665: Peripheral Neuropathies: Clinical Manifestations
- Page 666: Peripheral Neuropathies: Metabolic, Toxic and Nutritional
- Page 666: Symptoms of Dysautonomia With Polyneuropathies
- Page 667: Peripheral Neuropathy Caused by Heavy Metal Poisoning
- Page 668: Mononeuritis Multiplex with Polyarteritis Nodosa
- Page 670: Dysproteinemia (Amyloid Neuropathy)
- Page 672: Neuropathic Foot (Charcot Neuropathy)
- Page 674: AIDP (Guillain-Barre Syndrome)
- Page 675: Guillain-Barre Syndrome: Electrophysiologic Findings and Clinical Manifestations
- Page 676: Guillain-Barre
- Page 676: Tick Embedded in Scalp Causing Tick Paralysis
- Page 679: Spinal Nerve Origin: Sensory Components
- Page 680: Hereditary Sensory Neuropathy
Neuromuscular Transmission Disorders
- Page 685: Somatic Neuromuscular Transmission
- Page 685: Myasthenia Gravis: Clinical Manifestations
- Page 686: Neuromuscular Neurotransmission
- Page 687: Acetylcholine Receptor and Neuromuscular Junction
- Page 688: Thymoma
- Page 689: Pharmacology of Neuromuscular Transmission
- Page 692: Physiology of Neuromuscular Junction
- Page 693: Lambert-Eaton Syndrome
- Page 694: Neuromuscular Manifestations of Bronchogenic Carcinoma
Myopathies
- Page 700: Myopathies Related to Disorders of Potassium Metabolism
- Page 702: Myotonia Congenita (Thomsen Disease)
- Page 703: McArdle Disease
- Page 704: Myoglobinuric Syndromes
- Page 705: Carbohydrate Metabolism of the Muscle Cell
- Page 706: Regeneration of ATP for Source of Energy in Muscle Contraction
- Page 708: Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy: Muscle Biopsy Specimens
- Page 709: Floppy Baby
- Page 710: Myotonic Dystrophy
- Page 711: Sarcoglycan Complex and Sarcomere Proteins
- Page 712: Duchenne's Muscular Dystrophy
- Page 712: Duchenne's Muscular Dystrophy
- Page 713: Other Types of Muscular Dystrophy
- Page 718: Polymyositis and Dermatomyositis
- Page 718: Laboratory Studies in Neuromuscular Diseases: Electromyography and Serum Enzymes
- Page 719: Malignant Hyperthermia
- Page 719: Severe Pulmonary Fibrosis
- Page 721: Polymyositis and Dermatomyositis
- Page 722: Muscle Biopsy: Technique
- Page 723: Sections From Muscle Biopsy Specimens
- Page 725: Hypokalemia Associated Myopathy
- Page 726: Cushing's (Hypercortisolism)
- Page 727: Primary and Secondary Adult Myxedema
- Page 728: Basedow-Graves