Netter's Essential Systems-Based Anatomy
Author: Virginia Lyons
ISBN: 9780323694971
- Page 2: Computed tomography (CT) and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)
- Page 3: Anatomical Position and Body Planes
- Page 5: Body Regions
- Page 7: Terms of Relationship
- Page 9: Terms of Movement
- Page 10: Subcutaneous injections
- Page 11: Cross Section of Skin
- Page 12: Bursitis
- Page 13: Fascia, Synovium and Serous Membranes
- Page 14: Lymphangitis
- Page 15: Lymphatic System: Organization
- Page 17: Anatomical Variation
- Page 23: Nervous System: Organization
- Page 25: Neurons
- Page 27: Brain and Spinal Cord
- Page 28: Meningitis and Epidural Hematoma
- Page 29: Meninges
- Page 30: Common Sites of Cerebrovascular Occlusive Disease
- Page 31: Arterial Supply of the CNS
- Page 33: Venous Drainage of the CNS
- Page 35: Nervous System: Organization
- Page 36: Cavernous sinus thrombosis
- Page 37: Cranial Base
- Page 39: CN I, Olfactory nerve
- Page 40: Effects of Pituitary Tumors of the Visual Apparatus
- Page 41: CN II, Optic nerve
- Page 42: Damage to Oculomotor Nerve CN III (Oculomotor Palsy, Trochlear Palsy, Abducens Palsy)
- Page 43: CN III, Oculomotor nerve; CN IV, Trochlear nerve; CN VI, Abducens nerve
- Page 44: Trigeminal neuralgia (Shingles; Herpes Zoster)
- Page 45: CN V, Trigeminal nerve
- Page 46: Central Versus Peripheral Facial Paralysis
- Page 47: Facial nerve (VII)
- Page 48: Acoustic Neuroma
- Page 49: Vestibulocochlear (VIII) Nerve
- Page 50: Oral Cavity Inspection of Oral Cavity
- Page 51: Glossopharyngeal Nerve (IX) and Otic Ganglion
- Page 52: Neurogenic Disorders of Mouth and Pharynx
- Page 53: Vagus Nerve (X): Schema
- Page 54: Clinical Findings in Cranial Nerve XI Damage
- Page 55: Accessory Nerve (XI): Schema
- Page 56: Neurogenic Disorders of Mouth and Pharynx
- Page 57: Hypoglossal (XII) Nerve Hypoglossal Nerve (XII) Hypoglossal Nerve (XII): Schema
- Page 59: Spinal Nerves
- Page 61: Spinal Nerve Orientation
- Page 63: Neurons in Spinal Nerves
- Page 65: Sympathetic Nervous System
- Page 67: Sympathetic Neurons
- Page 69: Parasympathetic Nervous System: Schema
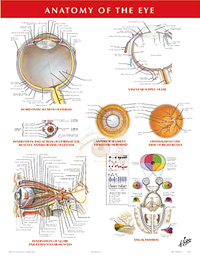
- Page 70: Myopia and Other Refractive Errors
- Page 71: Eye
- Page 72: Conjunctivitis
- Page 73: Orbit, Eyelids and Lacrimal Apparatus
- Page 75: Contents of the Orbit: Muscles
- Page 76: General Testing of Extraocular Muscles
- Page 77: Extrinsic Eye Muscles (continued)
- Page 78: Assessing Pupillary Size and Reaction
- Page 79: Nerves of Orbit
- Page 80: Intrinsic Arteries and Veins of Eye
- Page 81: Arteries and Veins of Orbit and Eyelids
- Page 82: Acute Otitis Externa and Media
- Page 83: Acute Otitis Externa and Media
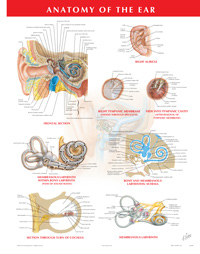
- Page 84: Pathway of Sound Reception
- Page 85: Middle Ear
- Page 86: Cochlear Implant
- Page 87: Inner Ear
- Page 97: Musculoskeletal System
- Page 98: Joint and Articular Changes
- Page 99: Joints
- Page 101: Features of Skeletal Muscles
- Page 102: Premature Suture Closure
- Page 103: The Skull
- Page 104: Mandibular Dislocation
- Page 105: Superficial Facial Muscles and Scalp
- Page 107: Deep Facial Muscles and Temporomandibular joint
- Page 108: Veins of Oral and Pharyngeal Regions Venous Drainage of the Mouth and Pharynx
- Page 109: Vasculature of the Face
- Page 110: Circulation: Palpation of Carotid Pulse
- Page 111: Regions and Fascia of the Neck
- Page 113: Muscles of the Neck
- Page 115: Vasculature and Nerves of the Neck
- Page 116: Facial Trauma: Broken Jaw and Jaw Exam
- Page 117: Lymph Vessels and Nodes of Head and Neck Lymphatic Drainage of Mouth and Pharynx
- Page 118: Kyphosis, Scoliosis, Lordoctic posture during pregnancy
- Page 119: Vertebral Column
- Page 121: Regional Types of Vertebrae
- Page 122: A herniated or ruptured disc
- Page 123: Joints and Ligaments of the Vertebral Column
- Page 125: Back Muscles
- Page 126: Shoulder separation (shoulder dislocation; Testing sensation)
- Page 127: Osteology of the Shoulder
- Page 129: Muscles of Rotator Cuff
- Page 130: Rotator Cuff Disease
- Page 131: Muscles of the Shoulder: Scapula
- Page 133: Vasculature of the Shoulder and Axilla
- Page 135: Nerves of the Shoulder and Axilla
- Page 136: Radial head subluxation (RHS)
- Page 137: Osteology of the Arm and Elbow joint
- Page 139: Muscles of the Arm
- Page 140: Sphygmomanometer (Blood pressure, Venipuncture)
- Page 141: Vessels of the Arm
- Page 142: Radial nerve compression
- Page 143: Nerves of the Arm
- Page 144: Colles fracture
- Page 145: Osteology of the Forearm, Wrist and Hand
- Page 147: Muscles of the Forearm: Anterior Compartment
- Page 149: Muscles of the Forearm: Posterior Compartment
- Page 150: Carpel tunnel syndrome
- Page 151: Carpal Tunnel and Anatomical Snuff Box
- Page 152: Proximal Compression of Median Nerve
- Page 153: Vasculature and Nerves of the Forearm
- Page 155: Intrinsic Muscles of Hand
- Page 156: Autogenous zones (Dermatomes)
- Page 157: Vasculature and Nerves of the Hand
- Page 159: Osteology and Fascia of the Trunk
- Page 159: Scarpa’s fascia
- Page 161: Muscles of the Trunk
- Page 163: Vasculature of the Trunk
- Page 165: Nerves of the Trunk
- Page 166: Inguinal hernia
- Page 167: Inguinal Region
- Page 168: Hip dislocations
- Page 169: Osteology of the Thigh and Hip
- Page 171: Osteology of the Gluteal Region
- Page 173: Muscles of the Thigh and Gluteal Region: Anterior and Medial Compartments
- Page 175: Muscles of the Thigh and Gluteal Region: Posterior Compartment
- Page 176: Hamstring Strain (Avulsion fracture)
- Page 177: Trendelenberg Test and Iliotibial Tract Band Syndrome
- Page 178: Femoral hernia
- Page 179: Vasculature of the Thigh and Gluteal Region
- Page 180: Sciatca (Piriformis Syndrome; Meralgia Paresthetica)
- Page 181: Nerves of the Thigh and Gluteal Region
- Page 182: Osteoarthritis
- Page 183: Knee Joint
- Page 184: Fractures
- Page 185: Osteology of the Leg
- Page 186: Major Sprains and Sprain Fractures
- Page 187: Osteology of the Foot and Ankle joint
- Page 189: Muscles of the Leg: Anterior and Lateral Compartments
- Page 191: Vasculature of the Leg
- Page 192: Chronic venous insufficiency (Varicose veins; Posterior Tibial Pulse)
- Page 193: Vasculature of the Leg
- Page 194: Foot drop (Compression)
- Page 195: Nerves of the Leg
- Page 196: Pedal Pulse
- Page 197: Dorsum of the foot
- Page 198: Plantar Fasciitis
- Page 199: Plantar Surface of the Foot: Layer 1
- Page 201: Plantar Surface of the Foot: Layers 2, 3, and 4
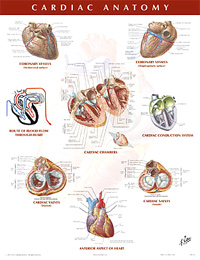
- Page 207: The Cardiovascular System
- Page 208: Right Atrium and Ventricle
- Page 209: Pericardium
- Page 210: Atrial septal defect and ventricular septal defect
- Page 211: Heart
- Page 212: Cardiac Auscultation: Precordial Areas of Auscultation
- Page 213: Heart valves
- Page 215: Right Atrium and Ventricle
- Page 217: Left Atrium and Ventricle
- Page 218: Coronary Artery Disease (CAD)
- Page 219: Arteries and Veins of the Heart Coronary Arteries and Cardiac Veins
- Page 220: Radiograph of Chest
- Page 221: Conduction system
- Page 221: Imaging of the Heart (Axial CT Scan of Heart)
- Page 222: Cardiac Pacemakers
- Page 224: Angina Pectoris
- Page 225: Innervation of the Heart
- Page 227: Pulmonary Circulation
- Page 228: Pedal Pulse (Arterial pulse; Dorsalis pedis pulse)
- Page 229: Systemic Circulation
- Page 230: Patent Ductus Arteriosus
- Page 231: Fetal Circulation
- Page 237: The Respiratory System
- Page 238: Histology and Physiology of Nasal Cavity and Sinuses
- Page 239: Nasal Skeleton and Paranasal Sinuses
- Page 240: Histology and Physiology of Nasal Cavity and Sinuses
- Page 241: Nasal Cavity
- Page 242: Epistaxis
- Page 243: Vasculature and Innervation of the Nasal Cavity
- Page 244: Obstructive sleep apnea
- Page 245: Pharynx and Larynx
- Page 246: Emergency Airway: Cricothyrotomy
- Page 247: Laryngeal Skeleton
- Page 248: Innervation of Larynx
- Page 249: Muscles and Innervation of the Larynx
- Page 250: Bronchial Asthma
- Page 251: Trachea and Bronchial Tree
- Page 252: Bronchopulmonary Segments
- Page 253: Lungs
- Page 254: PA and Lateral X-Rays: Superimposed Outlines of Lung Lobes
- Page 255: Imaging of the Lungs: Axzial CT Cross Section
- Page 256: Sternal angle (thoracentesis to remove pleural effusion)
- Page 257: Musculoskeletal Components of the Thorax
- Page 258: Diaphragmatic Hernia
- Page 259: Respiratory Diaphragm
- Page 261: Thoracic Cavity and Pleura
- Page 267: Gastrointestinal System: Organization
- Page 269: The Oral Cavity and Palate
- Page 271: Pharynx
- Page 272: Hiatal Hernia
- Page 273: Esophagus and Stomach
- Page 274: Pancreatic Cancer: Clinical Features
- Page 275: Duodenum and Pancreas
- Page 276: Cholelithiasis (Gallstones)
- Page 277: Liver and Biliary System
- Page 279: Jejunum and Ileum
- Page 280: Appendicitis
- Page 281: Colon
- Page 282: Fecal incontinence
- Page 283: Rectum and Anal Canal
- Page 284: Imaging of Digestive Viscera: Fluroscopic small bowel examination
- Page 285: Abdomen Axial 8
- Page 287: Blood Supply of Digestive Viscera
- Page 288: Causes of Portal Hypertension
- Page 289: Venous Drainage of Digestive Viscera
- Page 291: Innervation of Digestive Viscera
- Page 293: Lymphatics of Digestive Viscera
- Page 299: Endocrine System
- Page 300: Pituitary tumors (pituitary adenomas)
- Page 301: Pituitary Gland
- Page 302: Pharyngeal Pouch Abnormalities: Ectopic Thyroid
- Page 303: Thyroid and Parathyroid Glands
- Page 304: Insulin Delivery Methods
- Page 305: Pancreas
- Page 307: Adrenal Gland
- Page 312: Renal Biopsy
- Page 313: The Urinary System
- Page 314: Renal Vasculature - Variations in Renal Artery and Vein Variations in Renal Artery and Vein
- Page 315: The Kidney
- Page 316: Calculous Urinary Obstruction
- Page 317: Ureter
- Page 318: Urinary Incontinence: Bypass, Overflow, Stress, and Urge
- Page 319: Urinary Bladder and Urethra
- Page 320: Kidney Stones
- Page 321: Innervation of the Urinary System
- Page 327: The Reproductive System
- Page 328: Normal birth (Cardinal movements of labor)
- Page 329: Sex Differences of Pelvis: Measurements
- Page 330: Uterine prolapse (cystocele, rectocele)
- Page 331: Pelvic Support
- Page 332: Pelvic Peritonitis, Abscess
- Page 333: Female Reproductive Organs: Peritoneum and Adnexa
- Page 334: Pelvic exam (pap smear)
- Page 335: Female Reproductive Organs: Uterus and Vagina
- Page 336: Bartholin's Gland: Cysts
- Page 337: Female Perineum
- Page 338: Breast Cancer
- Page 339: Mammary Gland
- Page 340: Injuries to the Ureter
- Page 341: Female Vasculature
- Page 342: Pudendal nerve block (block anesthesia)
- Page 343: Female Innervation
- Page 345: Female Lymphatics
- Page 346: Vasectomy
- Page 347: Male Reproductive Organs, Scrotal Contents
- Page 348: Diseases of Prostate: Benign Prostatic Hypertrophy (BPH)
- Page 349: Prostate and Seminal Vesicles
- Page 351: Male Perineum
- Page 352: Varicocele, Hematocele, Torsion
- Page 353: Male Vasculature
- Page 355: Male innervation
- Page 357: Lymph Vessels and Nodes of Pelvis and Genitalia: Male Lymphatic Drainage of Pelvis and Genitalia